Photo credit: Shutterstock
2023 will be the year when tech advances, ranging from generative AI to cloud-native security, will reshape industries and fuel innovations.
For the fifth year running, Alibaba Group’s research institute DAMO Academy laid out its predictions in an in-depth report mapping out the year ahead.
“The innovation driven by the advancement of technologies and their industry-specific application has become an irreversible trend,” said Jeff Zhang, Head of DAMO Academy.
The academy developed its definitive list of tech trends by reviewing research materials and conducting interviews with nearly 100 subject matter experts. In doing so, DAMO Academy scientists considered a myriad of factors, including the impact of the theories, tech feasibility, degree of industrialization, and social values.
Scroll down to see the tech trends that DAMO Academy is banking on for 2023:

AI Gets Creative
Generative AI is revolutionizing how people conceive of creativity, turning anyone with a smartphone into an art curator.
Instead of analyzing existing data, generative AI creates new and original content based on machine learning algorithms trained on previous work. Developers have used it to generate images or texts, program code, paintings and illustrations, and even videos and audio.
In the next three years, generative AI will develop content creation capabilities on a par with humans to facilitate digital content creation, said DAMO Academy.
A whole infrastructure and ecosystem based on generative AI will come into being to make it easier for people with non-tech backgrounds to access the models and services.

When Math Met Machine Learning
Decision optimization will receive a boost from machine learning to help companies make better business decisions in 2023.
Fears of the pandemic persist, while risks from economic uncertainty are rising. Corporations are trying to combine mathematical optimization with machine learning to find the best solution in an ever-changing volatile situation.
Ride-hailing platforms have relied on decision intelligence for driver dispatch. And factories have tapped it to schedule production for minimal downtime. DAMO predicts that decision intelligence powered by machine learning will play a greater role in carbon reduction programs.
For example, due to the unpredictable nature of renewable energy, utility companies had difficulty integrating renewable energy into the power grid. By combining the power of optimal mathematical models and AI algorithms, the dual-engine approach can help utility companies achieve more accurate power generation forecasts to reduce carbon emissions and achieve stable operations.

Security First on the Cloud
By 2025, over 95% of new digital workloads will be deployed on cloud-native platforms, up from 30% in 2021, according to a 2021 report by research firm Gartner.
In the past, companies have designed their security system with a business-first approach. But the increased deployment of cloud-native applications creates the need for more advanced security applications.
DAMO Academy said in the future, companies will pursue a cloud-native security approach that builds security into all stages of the software development life cycle. Instead of having a security system as an add-on, security would be integrated into product design from day one.

AI’s Sixth Sense
Just like humans have developed multiple senses to explore the world, AI has grown capable of learning from different sources to take action.
Multi-modular pre-training models combine various data types, including image, text, speech, and numerical data, to understand the world. In doing so, they are taking over the field of AI. Unlike their single-mode predecessors, these AI models will devour many different data types and simultaneously process them.
“Pre-trained multimodal models outperform mono-modal models in terms of understanding, retrieval, generation, and question answering,” said Huang Fei, head of the Language Technology Lab of DAMO Academy.
By giving companies access to advanced models and data analytics, multi-modular pre-training models will be the key to boosting corporate productivity in the future, said DAMO.
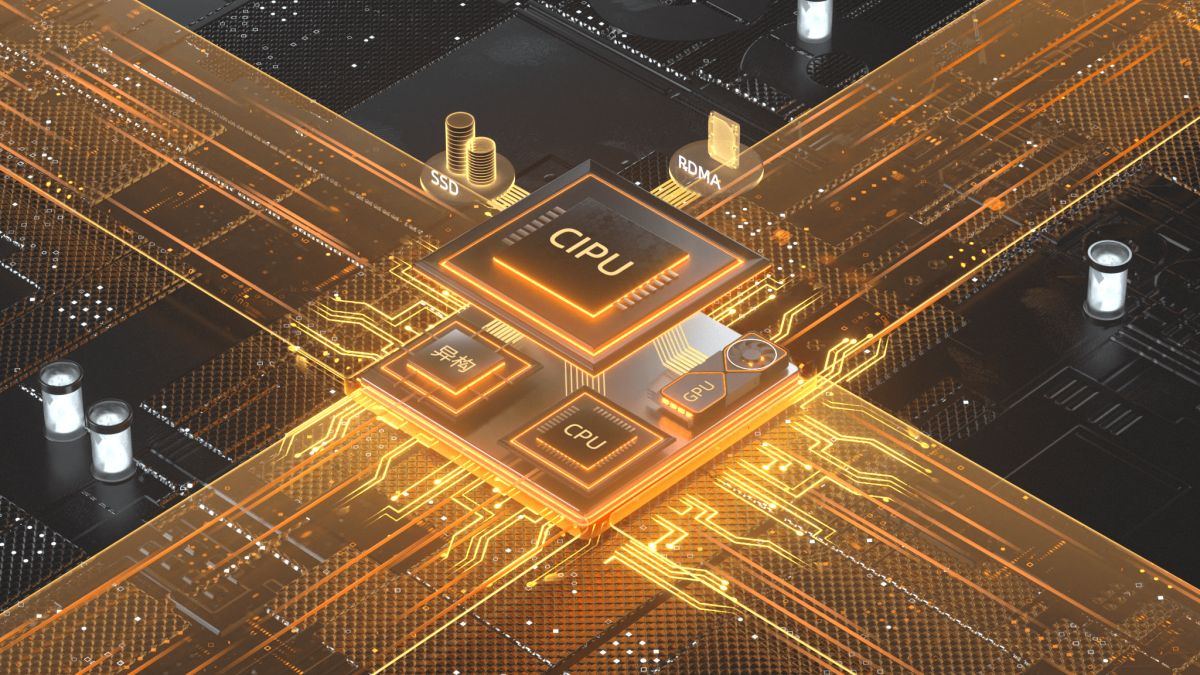
Move Over CPU
The exponential growth in data processing needs has made centralized processing units (CPU) inadequate. Companies have invented new server hardware to address the demand to process higher data volume at lower latency.
Enter Alibaba Cloud’s Cloud Infrastructure Processing Unit.
By offloading a wide range of virtualization functions associated with storage, networking, and security from the CPU onto dedicated hardware, it can service more intensive uses for big data and artificial intelligence.
In the next three years, cloud computing will embrace a new infrastructure system centered around CIPU, said DAMO. It will create development opportunities for the research and development of core software and the specialized chip industry.
Always Cloudy, Please
Data centers are crucial to support resource-draining tasks like AI and machine learning. They provide large volumes of computing, storage and energy while allowing clients to pay as they go.
But cloud providers do not offer guaranteed network resources to clients. The high variability in the performance provided by cloud networks often leads to unpredictable application performance.
“When the computing power network evolves to become a key part of the nation’s infrastructure, there is no doubt that the demand for predictability will become the number one priority,” DAMO Academy scientists wrote in the report.
The report estimates that in the next two to three years, a predictable network powered by edge-network integration will become the norm.
Phone! Lights! Action!
Ever wonder why your smartphone can take great photos and videos? The credit goes to computational imaging, which will change the way we see our world, according to DAMO Academy.
“The emergence of computational imaging is set to transform the way human beings and machines perceive the world,” Jiamin Wu, Assistant Professor in Tsinghua University’s department of automation, noted in the report.
Powered by technology such as artificial intelligence and signal processing, computational imaging makes it possible for smartphones to perform like professional cameras – even without large sensors and powerful lenses.
Computational imaging is revolutionizing imaging applications from portrait lighting to vibration reduction, making high-tech tools available in the palm of your hand at a fraction of the price.
Chiplets
The conventional wisdom is that to make computer chips faster, designers need to pack more transistors onto one piece of silicon and make them bigger.
But with the surging volume of data processing, it would be challenging to produce larger chips to provide the computing horsepower. Chip developers instead chose an alternative approach to break the chips into smaller pieces and stitch them together. Each part, dubbed a chiplet, makes up a larger integrated circuit.
Chiplets are less prone to manufacturing defects and are less costly to produce because they are small. Chipmakers can also add or subtract chiplet on processors to customize the chips to suit their needs.
In 2022, the industry also introduced a new standard for chiplet-based processor designs. These small but mighty components will continue to transform chip research and development in the year ahead, according to DAMO Academy.

Making Memories
To make AI processing power-efficient, a new computing architecture called processing-in-memory is here to help.
The traditional architecture for computing systems uses separate processors and memory units to carry out data processing tasks. It requires data to be constantly moved back and forth between the processor and the main memory.
Processing in memory can overcome the data transfer by bringing processing directly to where data is stored, leading to a reduction in energy consumption and a boost in system performance.
DAMO Academy said processing in memory would become the mainstream computing architecture in the AI era. Developers have come up with compute-in-memory chips to power a wide range of AI applications, ranging from virtual and augmented reality to astronomy data computing.

A Tale of Two Cities
If you wonder how a mega city operates, check out its digital twin, or 3D virtual replicas of the city that gives you a glimpse of the real-time situation of its people, vehicles, and buildings.
Powered with technologies such as sensors and advanced analytics, urban planners can connect the real-time data of physical objects in the cities with their digital representation.
Singapore has created the world’s first digital twin of an entire country, allowing it to virtually test potential policy initiatives before implementing them in the real world, be it predicting road traffic or simulating energy use.
DAMO Academy said large-scale urban digital twins had achieved significant progress in traffic management, natural disaster prevention, and carbon emission management. In the future, they can help urban planners develop and test autonomous vehicles, drones and robots to build smart cities.